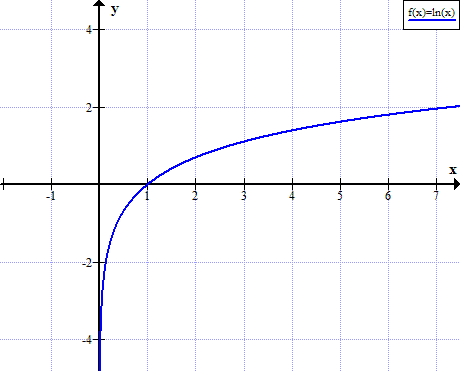
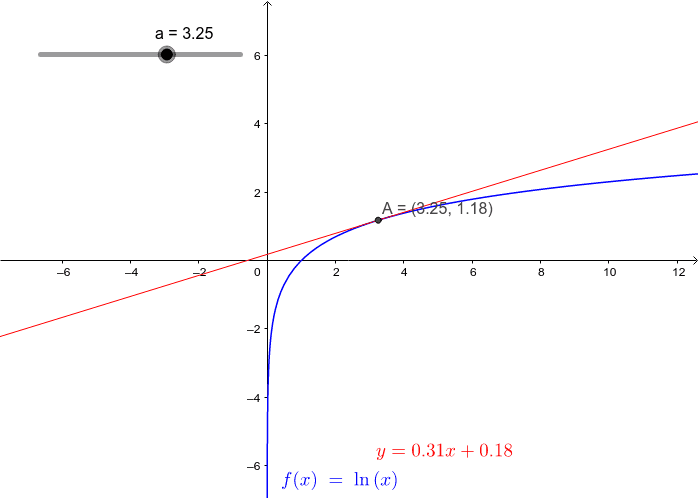
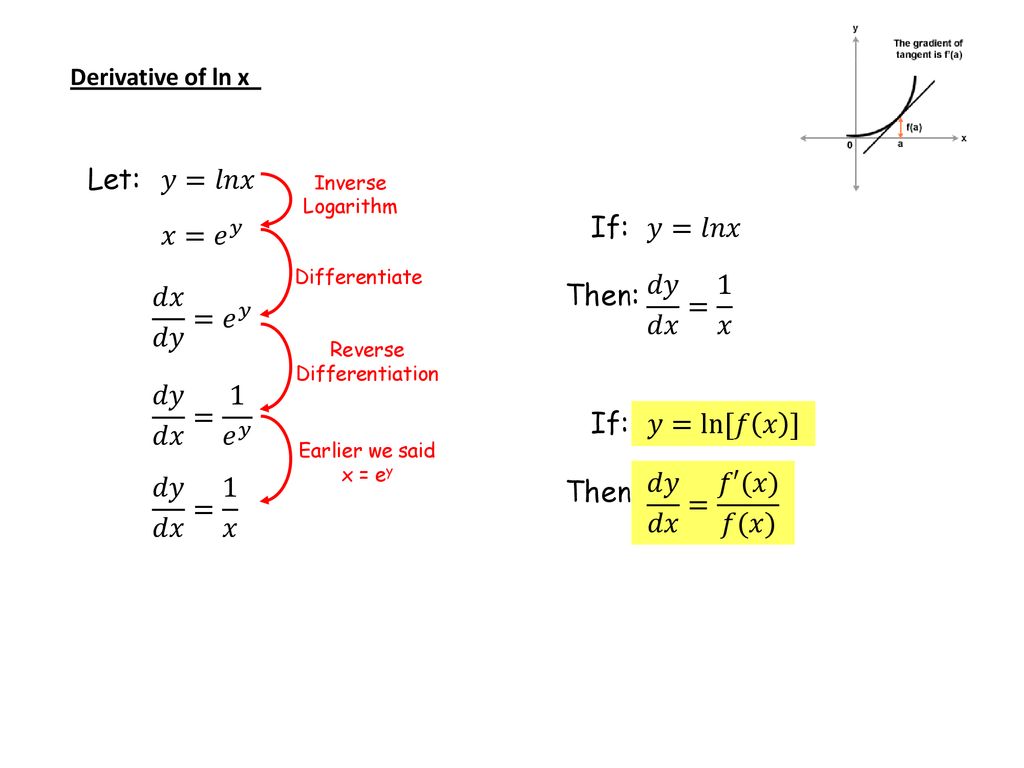
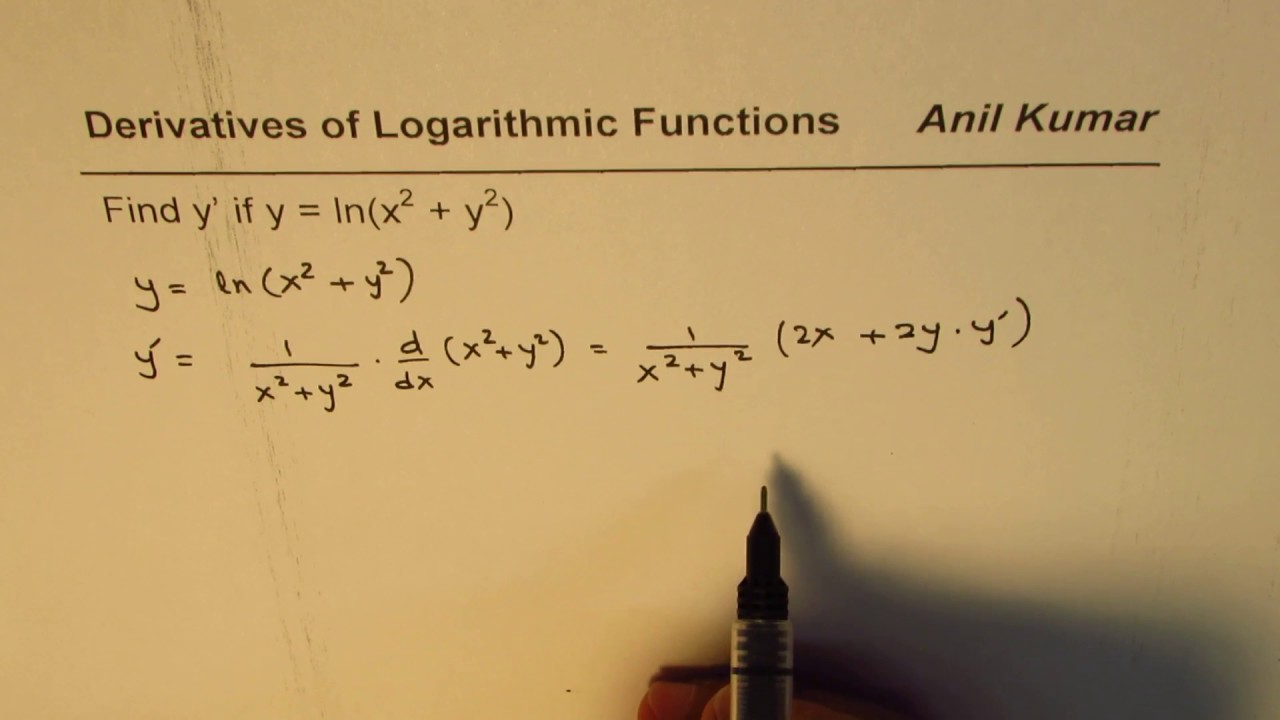![SOLVED: Given: y = (Inx) find dy/dx 1t (In ln? y = (In .)" In 1 = (Inc)"-1 [1 + x (lnz) (Inlnz)] y' = (lIn2)*+1[2 + lnx] None of these (In 2)" (1 + lnz) SOLVED: Given: y = (Inx) find dy/dx 1t (In ln? y = (In .)" In 1 = (Inc)"-1 [1 + x (lnz) (Inlnz)] y' = (lIn2)*+1[2 + lnx] None of these (In 2)" (1 + lnz)](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/66c9522b48a84466bc3c40a4c3f7e9f5.jpg)
SOLVED: Given: y = (Inx) find dy/dx 1t (In ln? y = (In .)" In 1 = (Inc)"-1 [1 + x (lnz) (Inlnz)] y' = (lIn2)*+1[2 + lnx] None of these (In 2)" (1 + lnz)
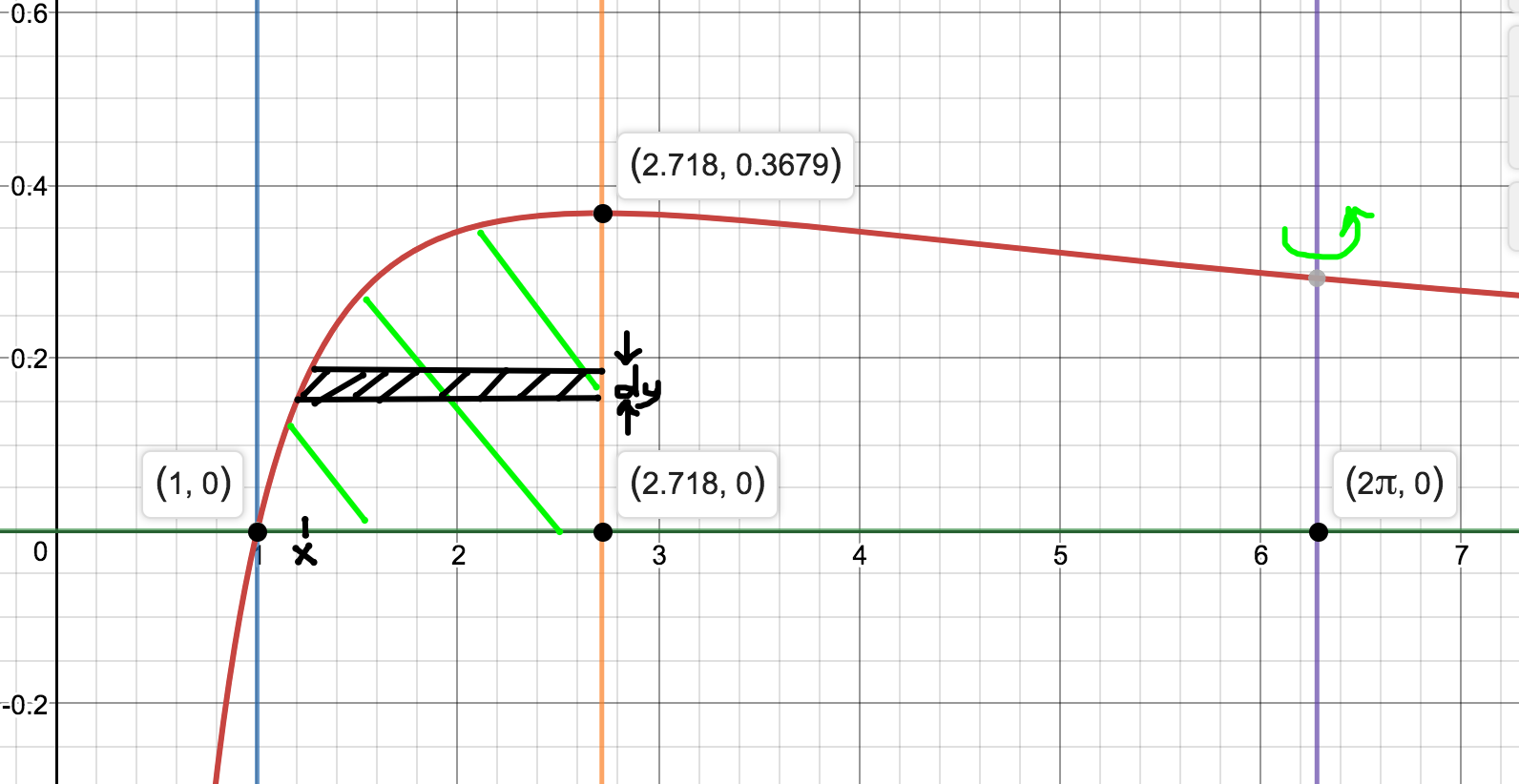
The region bounded by the curve y=ln(x)/x and the lines x=1, x=e, y=0 is rotated around x=2π. Find the volume of the solid generated. How would I go about solving this? Doesn't
How would I calculate the volume of an area bound by y=lnx, y=1, y=2, and x=0 if it was swung around the y axis? How can one find the limits of integration

SOLUTION: Set up, but do not evaluate, the integral which gives the volume when the region bounded by the curves y = Ln(x), y = 1, and x = 1 is revolved

algebra precalculus - Is there a solution to $y=\ln(x)+x$ which yields an answer in the form $x^2=...$ - Mathematics Stack Exchange

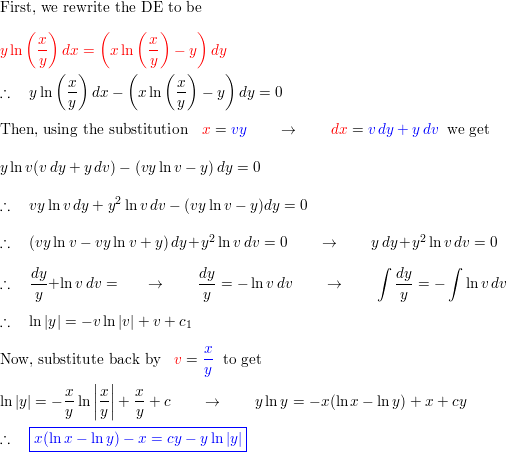


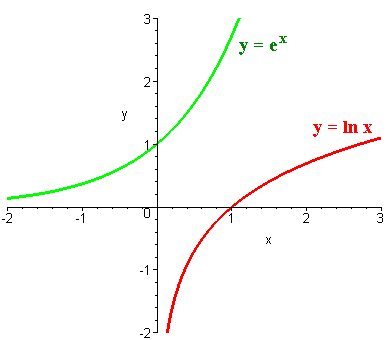
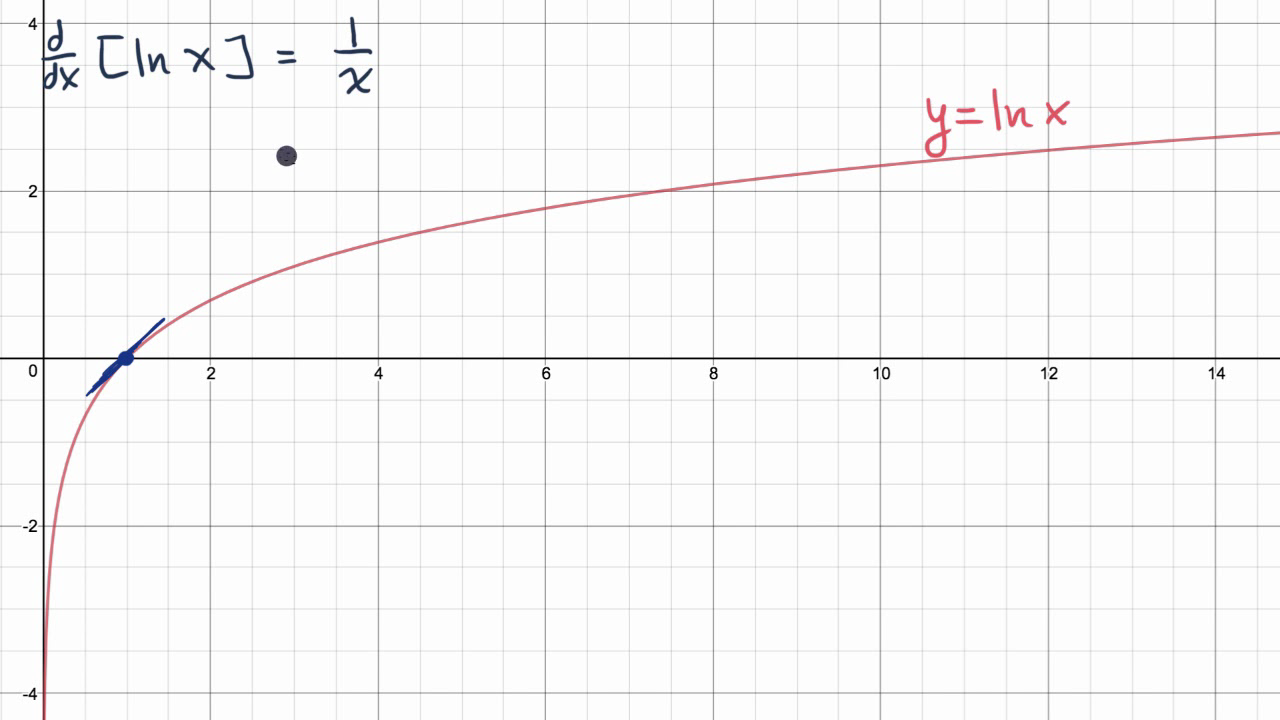
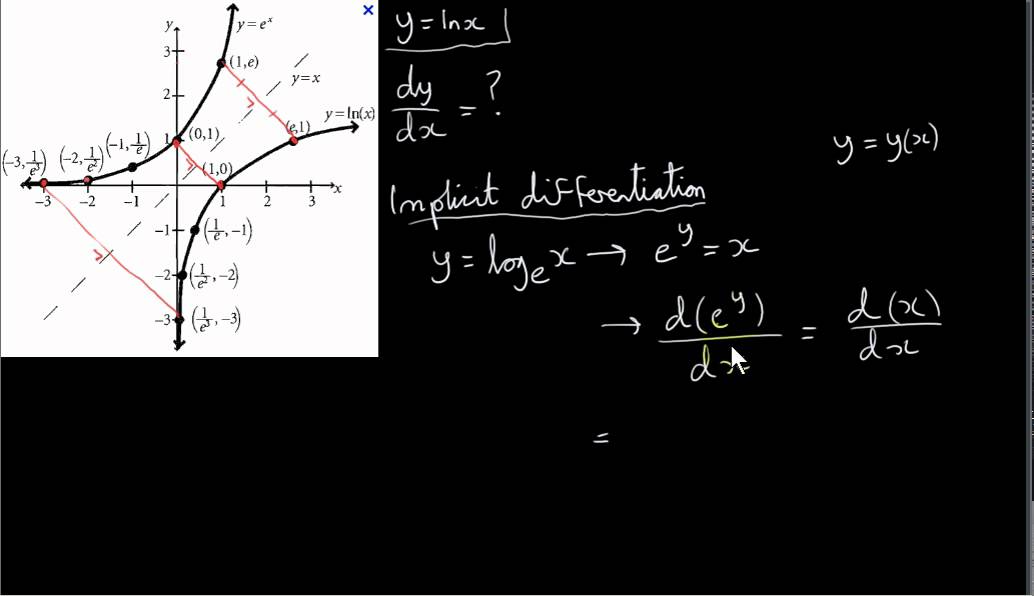


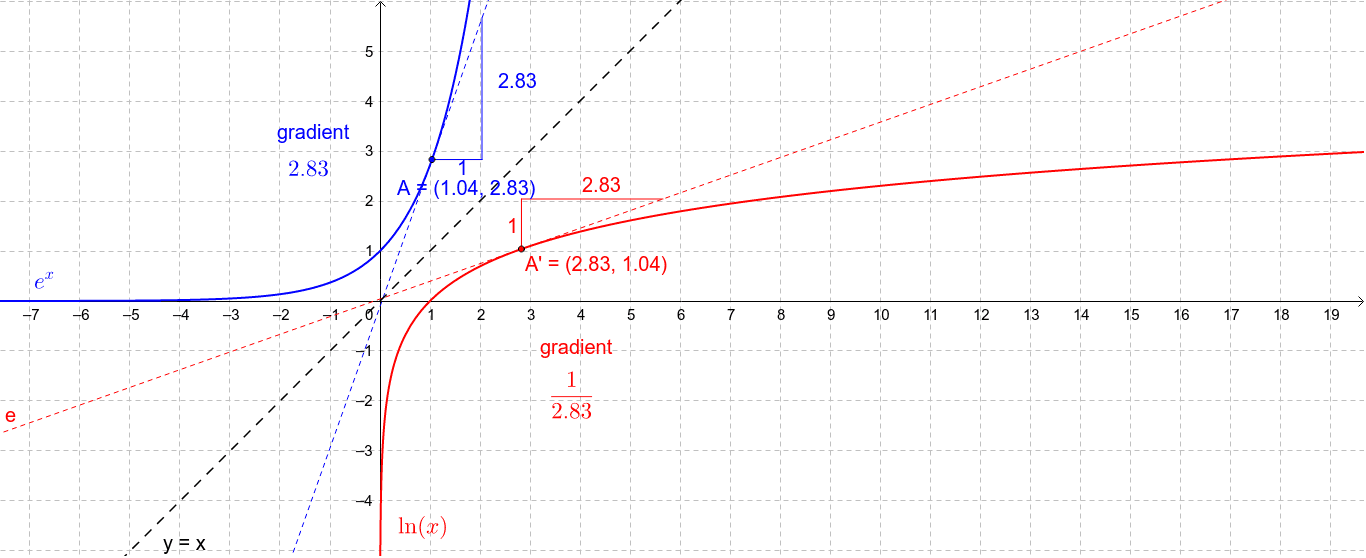



.gif)